At Chiropractic Singapore, we believe in empowering our patients with knowledge that enhances their health and overall quality of life. One of the most common questions we hear in our clinics is: Can inflammation cause fever? In this article, we explore this question in depth, break down what inflammation is, and how it impacts your body. We will also discuss the difference between acute and chronic inflammation, identify inflammatory markers, and provide tips on how to reduce inflammation in the body naturally. Whether you’re a health-conscious reader, a patient managing chronic pain, or a researcher exploring natural health modalities, this guide offers valuable insight.
What Is Inflammation?
Inflammation is the body’s natural response to injury, infection, or harmful stimuli. It is a protective mechanism that initiates healing and repair. But when inflammation becomes prolonged or mismanaged, it can lead to chronic health conditions.
Two Types of Inflammation:
Inflammation Types |
Inflammation Description |
Duration |
Examples |
|---|---|---|---|
Acute Inflammation |
Rapid onset inflammation in response to injury or infection | Short-term (days) | Cuts, colds, sore throat |
Chronic Inflammation |
Long-term inflammation often linked to health conditions | Months to years | Arthritis, diabetes, autoimmune disorders |
Understanding the acute and chronic inflammation difference is essential in identifying the root cause of discomfort and seeking appropriate care.
Can Inflammation Cause Fever?
Yes, inflammation can cause fever. When the immune system detects a threat such as a bacterial infection or tissue injury, it releases inflammatory chemicals called cytokines. These cytokines signal the hypothalamus in the brain to increase the body’s temperature set point, resulting in a fever.
Fever is one of the many signs that the body is fighting something internally. While it may be uncomfortable, it is a sign that your body is working to protect and heal itself.
Common Symptoms That May Accompany Inflammation-Induced Fever:
- Fatigue – a persistent, overwhelming sense of tiredness or low energy that doesn’t improve with rest, often due to the body’s immune system working overtime.
- Muscle aches – generalised soreness, stiffness, or discomfort in the muscles, which may feel tender to touch or worsen with movement.
- Chills or sweating – sudden changes in body temperature, including feeling cold despite warmth or sweating without physical exertion, as the body adjusts to immune signals.
- Headache – often a dull, pressure-like pain that may be felt across the forehead or temples, sometimes linked to inflammation in the nervous system.
- Loss of appetite – reduced desire to eat, often due to the body focusing on healing
- Fever caused by inflammation—also known as inflammation fever—often occurs alongside other systemic signs of immune response. At Chiropractic Singapore, we assess each patient thoroughly, looking at symptoms such as fever in conjunction with other signs of inflammation, to identify the best course of care.
Understanding Inflammatory Markers
Inflammatory markers are substances in the blood that indicate the presence of inflammation in the body. Your doctor may recommend blood tests to measure these markers if chronic inflammation or inflammation fever is suspected.
Common Inflammatory Markers:
Inflammatory Markers |
What It Indicates |
Notes |
|---|---|---|
CRP (C-Reactive Protein) |
General inflammation or infection | Often elevated in acute inflammation |
ESR (Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate) |
Chronic inflammation | Non-specific, but useful in monitoring trends |
Interleukins (e.g., IL-6) |
Immune system activity | Strongly linked to systemic inflammation |
TNF-α (Tumour Necrosis Factor alpha) |
Cytokine involvement in inflammation | Often targeted in autoimmune therapy |
These markers are especially useful in detecting silent or low-grade inflammation that may not present obvious symptoms.
Inflammatory Markers: Where to Get Tested in Singapore
You can get inflammatory marker blood tests at most major hospitals, general practitioner (GP) clinics, and diagnostic laboratories. Some options include:
- Public Hospitals: Singapore General Hospital (SGH), National University Hospital (NUH), Tan Tock Seng Hospital (TTSH)
- Private Hospitals: Mount Elizabeth Hospital, Gleneagles Hospital, Parkway East Hospital
- Diagnostic Labs: Raffles Medical Group, Healthway Medical, Fullerton Health, Quantum Diagnostics, SATA CommHealth
- Online Health Services: Some providers like Minmed, Homage, and Speedoc offer home blood testing with doctor consultations.
It’s best to consult a healthcare professional for recommendations based on your symptoms and medical history.
Muscle Inflammation: A Common Complaint
We see many patients at our clinics who are suffering from muscle inflammation. This may result from overuse, poor posture, injury, or stress. It can cause stiffness, pain, and reduced mobility.
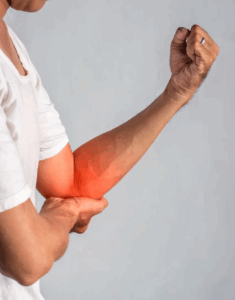
Common Signs of Muscle Inflammation:
- Swelling or tenderness – The area may feel sore or appear slightly swollen.
- Ongoing or recurring pain – Discomfort that persists or returns, especially after activity.
- Muscle weakness or fatigue – Reduced strength or early muscle tiredness.
- Limited flexibility or movement – Stiffness or difficulty moving the muscle fully.
- Pain with activity or pressure – Discomfort worsens when the muscle is used or pressed.
Through chiropractic adjustments, soft tissue therapy, and posture correction, we help manage inflammation, relieve pain, and restore function naturally and non-invasively.
Can Spinal Misalignment Cause Inflammation?
Yes, spinal misalignment can contribute to inflammation—both locally and systemically.
When the spine is not properly aligned, it can put abnormal stress on surrounding muscles, ligaments, joints, and nerves. This mechanical stress can lead to microtrauma and tissue irritation, triggering the body’s inflammatory response. Over time, if left uncorrected, spinal misalignments (also called subluxations in chiropractic care) may promote chronic inflammation, which may worsen pain, reduce mobility, and even affect your immune and nervous systems.

Possible Causes of Inflammation from Spinal Misalignment:
- Poor posture can cause inflammation – such as prolonged sitting, slouching, or “tech neck” from excessive screen time
- Injury or trauma can cause inflammation – including accidents, falls, or sports-related impacts
- Muscle imbalances can cause inflammation – where certain muscles overwork to compensate for weaker or underused areas
- Sedentary lifestyle can cause inflammation – limited movement reduces circulation and increases stiffness
- Repetitive strain or overuse can cause inflammation – frequent, small movements that place continuous stress on specific areas
- Chronic stress and tension can cause inflammation – which can cause sustained muscular tightness and joint restriction.
Chiropractic care focuses on correcting these misalignments to alleviate stress on the body and reduce inflammation naturally.
Inflammatory Foods to Avoid
Diet plays a critical role in either fuelling or fighting inflammation. Certain foods are known to trigger or worsen inflammatory responses in the body.
Common Inflammatory Foods:
Category |
Examples of Inflammatory Foods |
Why It Causes Inflammation |
|---|---|---|
Sugars |
Soft drinks, pastries, candy | Excess sugar increases insulin levels and triggers the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines. It also promotes oxidative stress and can disrupt gut health. |
Processed Meats |
Sausages, bacon, deli meats | These are often high in saturated fats, preservatives like nitrates, and advanced glycation end products (AGEs), all of which contribute to systemic inflammation. |
Refined Carbs |
White bread, pasta, rice | These break down quickly into sugar, spiking blood glucose and insulin levels, which can activate inflammatory pathways and contribute to insulin resistance. |
Trans Fats |
Margarine, packaged snacks | Artificial trans fats increase LDL (“bad”) cholesterol, lower HDL (“good”) cholesterol, and have been shown to increase levels of inflammatory markers like CRP. |
Additives |
Monosodium glutamate (MSG), artificial sweeteners | These can disrupt gut microbiota balance and may trigger immune responses in sensitive individuals, contributing to low-grade chronic inflammation. |
We always advise our patients to make mindful dietary choices. Cutting back on these foods can significantly reduce the inflammatory burden on your body.
How to Naturally Reduce Inflammation in the Body
Sustainable lifestyle changes can significantly lower chronic inflammation and support your body’s long-term health. Below are evidence-based strategies to reduce inflammation naturally and effectively:
Approach |
Why It Matters |
Practical Guidance |
|---|---|---|
Anti-Inflammatory Nutrition |
Nutrient-rich foods help neutralise oxidative stress and downregulate inflammatory pathways. | Eat more anti-inflammatory foods like leafy greens, berries, oily fish, olive oil, turmeric, and nuts. Cut back on processed foods and sugars. Learn to read nutrition labels and shop healthy in Singapore. |
Consistent Physical Activity Reduces Inflammation |
Movement enhances circulation, modulates immune function, and reduces inflammatory markers. | Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate exercise on most days—such as walking, stretching, swimming, cycling, or resistance training. |
Restorative Sleep Reduces Inflammation |
Sleep is essential for immune regulation and tissue repair; poor sleep is linked to elevated inflammation. | Target 7–9 hours of high-quality sleep per night. Establish a regular sleep schedule and create a calming bedtime routine.Aim for 7–9 hours of quality sleep each night by maintaining a consistent sleep schedule and creating a calming bedtime routine. Improve your rest with our guides on choosing the best pillow for your needs, ideal sleeping positions, and the best mattress for back pain. |
Stress reduction helps combat inflammation |
Chronic stress activates inflammatory pathways through hormonal and nervous system responses. | Incorporate mindfulness practices, such as meditation, breathwork, yoga, or nature walks. Prioritise activities that promote mental calm. |
Hydration Reduces Inflammation |
Adequate hydration supports detoxification, joint lubrication, and metabolic balance. | Drink sufficient water throughout the day. Limit intake of dehydrating substances like caffeine, alcohol, and sugary drinks. |
Chiropractic care helps reduce inflammation naturally |
Misalignments can place mechanical stress on joints, muscles, and nerves, contributing to inflammation. | At Chiropractic Singapore, care includes spinal adjustments, postural correction, and nervous system regulation—helping restore alignment, reduce stress, and enhance natural healing. |
Many of our patients have experienced improvements in mobility, reduced muscle tension, and even enhanced energy levels as their inflammation subsided. Chiropractic care can be an effective long-term strategy for both managing and preventing inflammation.
Medications Used to Relieve Inflammation in Singapore
While we focus on non-invasive and natural methods of care, we understand that medications may be necessary in certain situations. Several types of medicines are commonly available in Singapore to relieve inflammation.
Common Types of Anti-Inflammatory Medicines:
Types of Medicines |
Examples |
Details / Notes |
|---|---|---|
NSAIDs (Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs) |
Ibuprofen, Naproxen, Aspirin | Commonly used to reduce pain, fever, and inflammation by blocking COX enzymes. Available over-the-counter or by prescription. Long-term use may irritate the stomach or affect kidneys. |
Paracetamol (Acetaminophen) |
Panadol | Relieves pain and fever but has minimal anti-inflammatory effect. Gentler on the stomach, but high doses can affect the liver. |
Corticosteroids |
Prednisolone | Strong anti-inflammatories used for severe or chronic inflammation (e.g., autoimmune issues). Short-term use is typical due to potential side effects like weight gain or lowered immunity. |
Topical NSAIDs |
Diclofenac gel | Applied to skin over sore joints or muscles. Offers localized relief with fewer side effects than oral NSAIDs. |
COX-2 Inhibitors |
Celecoxib (Celebrex) | Targeted NSAIDs that reduce inflammation with less risk of stomach irritation. Often used for long-term conditions like arthritis. |
Always consult a licensed medical professional or pharmacist before starting any medication. It is important to use medicines responsibly, especially if you have other health conditions or are on other treatments.
When to Get Help for Inflammation
Persistent or unexplained symptoms may be your body’s way of signalling ongoing inflammation that requires attention. You should consider seeking professional care if you experience:
- Recurrent fevers – frequent episodes without a clear cause
- Ongoing fatigue – tiredness that doesn’t improve with rest
- Chronic joint or muscle pain – stiffness, soreness, or discomfort that interferes with daily life
- Digestive issues – bloating, cramps, irregular bowel movements, or food sensitivities
- Skin flare-ups – such as eczema, psoriasis, or other inflammatory skin conditions
These symptoms may seem unrelated at first, but together they can point to a deeper, systemic imbalance driven by inflammation.
Don’t wait for symptoms to worsen. Early intervention allows for more effective management and can prevent long-term complications. A comprehensive evaluation can help uncover the root causes and guide you toward a targeted, natural, and sustainable recovery plan.
Why Choose Chiropractic Singapore to Address Your Inflammation?
At Chiropractic Singapore, we go beyond managing back pain. Our mission is to help you live a healthier, pain-free life by addressing the underlying causes of discomfort—including inflammation, which is often overlooked in conventional care.
How Chiropractic Care Helps Combat Inflammation
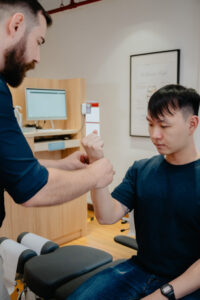
- Reduces nerve and joint stress that helps prevent inflammation – Spinal misalignments can place pressure on nerves and joints, triggering inflammatory responses. Chiropractic adjustments help restore proper alignment, reducing this mechanical strain.
- Supports the nervous system that helps prevent inflammation – A balanced spine improves communication between the brain and body, enhancing immune regulation and helping the body respond appropriately to inflammation.
- Improves circulation and mobility that helps prevent inflammation – By relieving tension and restoring range of motion, chiropractic care promotes better blood flow and nutrient delivery, aiding tissue repair and reducing local inflammation.
- Drug-free and non-invasive – Safe for long-term use, chiropractic care offers a natural approach to managing inflammation without relying on medication.
- Prevents recurrence – Regular care, combined with posture correction and lifestyle advice, helps minimise triggers of chronic inflammation over time.
Book Your Appointment Today
If you’re experiencing symptoms that may be linked to inflammation—or simply want to move, feel, and live better—chiropractic care could be the missing link in your wellness journey.
Take the first step towards a healthier, more balanced life.
Book your consultation with Chiropractic Singapore today.
Let us help you feel better, move better, and live better—naturally.